Countries have been buying the idea of digital currency as a legal tender. Unlike traditional paper bills or metal coins, these digital currencies are secure tokens that the country’s central bank directly issues.
Imagine being able to pay for any commodity, travel fee or easy swap of your currency with your phone and internet with ease and speed. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) promise to redefine how people access money.
Since the advent of Bitcoin and other altcoins, and the way they are transforming the traditional finance system, governments and financial institutions seem keen to adopt CBDCs to modernise existing payment systems, facilitate financial inclusion, and increase the level of transparency in financial transactions.
In this article, we examine the reason behind the use of CBDCs, the technology which enables the implementation of them, their strengths and weaknesses, as well as the issues that they face.
What are Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)?
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are types of digital money issued by a nation’s central bank. It can be compared with cryptocurrencies, with the exception that the central bank sets its value, which is equal to the nation’s fiat currency.
Instead of being a private coin like Bitcoin, CBDC is issued by a central bank. In contrast with crypto assets, which see significant value fluctuations for a variety of reasons, here the currency would be issued by the government, guaranteeing its stability.
In simple terms, CBDCs are:
- Conventional currency in a digital format.
- Issued and overseen by the central bank of a nation.
- Impact in terms of value and supply by a nation’s central bank, trade surpluses, and monetary policies.
- Based on a digital ledger, and it might or might not make use of a distributed ledger or blockchain technology.
Some countries, such as China and Nigeria, have initiated steps to adopt their CBDC like the digital yuan and eNaira, respectively and have also initiated pilot programs. However, others are still weighing the risks against the benefits.
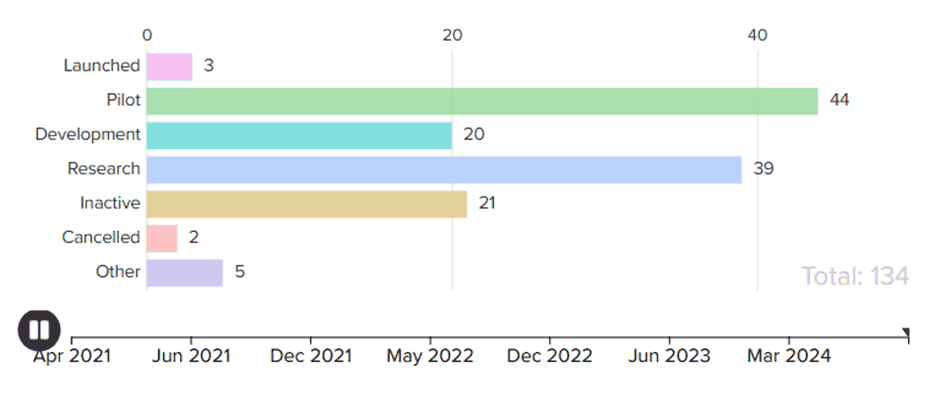
CBDC Launches From Counties – Source: Atlantic Council
Apart from this, the Atlantic Council’s CBDC Tracker says that 44 major countries including India, Russia, Brazil, Iran and others are currently involved in the CBDC pilot phase.
Motivation Behind CBDCs
According to the Harvard Business Review (HBR) study in 2021, over 90% of the money in circulation today is digital, and the transformation has reduced the use of cash.
Many countries are buying the idea of CBDC because of its potential innovations and financial transformational abilities. Some of the reasons driving this adoption include:
1. Payment System Efficiency and Safety
CBDCs have the ability to minimise middlemen in the payment process, improving the way transactions work, as well as reduce the fees tied to these transactions. Central banks look to bring out a swift and secure way of transacting that can enhance the quality of domestic payment systems in response to their objectives.
2. Promoting Financial Inclusion
For regions that do not have traditional forms of banking easily available, CBDCs act as an avenue for bridging the financial gaps. This approach ensures that central banks are able to provide a fully-fledged digital currency regardless of where they reside. It allows them to explore the digital economy.
3. Combating Criminal Activities by Maintaining Transparency
When it comes to illicit activities, CBDC can help track obscured information, thus alleviating the shortcomings that are present today. This embedded transparency also aids in regulation enforcement and diminishes the chances of financial crimes propagating altogether.
4. Cross-Border Transactions
It facilitates and processes cross-border payments in a more efficient way that translates into reduced costs and speedier settlement time- a differentiating quality in such an integrated economy.
The International Monetary Fund indicates that CBDCs can improve the provision of financial services since there would be scope for more currencies to be utilised, and increase the effectiveness of payment systems.
Global Trends in CBDC Development
Many countries are looking into the possibility of developing and executing Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) in the current financial system, with China leading the race with its digital yuan. Presently, over 134 nations have prepped to unveil their own CBDCs, amounting to up to 98% of the total economy around the world.
At present, there are 66 nations at the matured stage of developing CBDCs, and the number of pilot programs and applying countries are growing from both the developing and developed economies. China remains the first in the digital currency race with its e-CNY, which has a transaction turnover of $56 Billion as of September 2024. This sets the pace for other countries that aspire to introduce their currencies in digital form.
Other than China, in Europe, the development of a digital Euro by the European Central Bank is in progress as well. The main goal with the Euro being designed is to reinvent the financial climate across the euro area.
Similarly, since its launch in 2021, Nigeria’s eNaira has significantly progressed and has become an integral part of the country’s strategy to enhance its financial inclusion as it provides potential buying services for the marginalised people.
Even in the U.S., the debate about the digital dollar is politicised. The Fed is looking into a possible rollout of a U.S. central bank digital coin, but the discussions on privacy issues as well as excessive government control have impeded adequate progress in this direction.
The vision is, however, different for the Bank of England, which is developing a wholesale CBDC, geared towards interbank large-value transactions, suggesting that countries are adopting a mix of retail and wholesale for their CBDCs as per their specific requirements.
Canada is also pursuing cross-border projects. mBridge is a good example and is being implemented by China, the UAE, Hong Kong and Thailand for carrying out safe and quick cross-border transactions through the use of CBDC. This is indeed a strong collaborative initiative as it attempts to solve the problems regarding cost and efficiency while using international payment systems.
Technologies Behind CBDC
CBDC relies on advanced technology for it to work efficiently towards achieving its goals to maintain security, scalability, efficiency, and transparency. These innovative technologies include:
1. Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is the very first technology applied and is usually referred to in the context of blockchain technologies. It allows ‘transactions’ to be reliably appended across peer-to-peer networks.
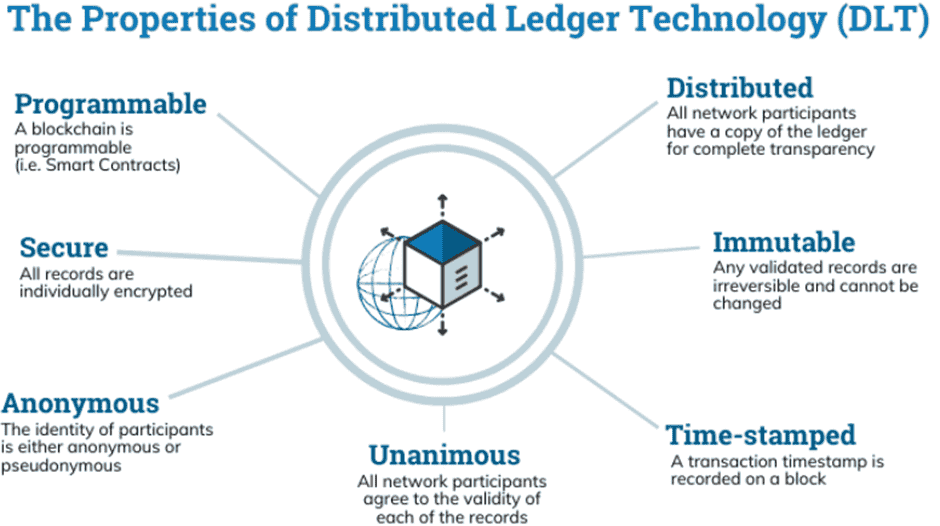
Source: Researchgate
The majority of central banks favour permissioned DLT systems where only pre-identified individuals are allowed to validate transactions, thus ensuring more control and regulatory compliance. This structure optimises real-time settlements, fraud detection and transaction traceability.
2. Smart Contracts
In certain CBDC systems, smart contracts function as self-fulfilling agreements containing terms which are automatically executed. This eliminates the necessity to have an intermediary which brings down the overall cost for the transaction.
Similarly, the required scale and durability for large amounts of transactions are provided by cloud computing and detection of fraud, economic surveillance and tailored financial services which are powered by artificial intelligence and complex data analytics are completed.
3. Security and Privacy
In order to achieve security and privacy, Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDC’s) utilise sophisticated encryption techniques, as well as digital identity systems. Public-private key encryption and zero-knowledge proofs are perfect examples of crypto-technologies that work together to keep the information contained in the transaction secure.
Digital identity systems, such as KYC (Know Your Customer) and biometrics, are placed into practice to mitigate the risk of fraudulent activities and improve regulation.
Potential Benefits and Challenges of CBDC Implementation
| Benefits | Challenges |
| The ability of CBDCs to offer a safe and dependable method of digital payment and remittance is one of its key benefits. | There might occur various monitoring problems in financial transactions, which would pose security and privacy issues. |
| CBDCs can be incorporated into current payment systems and utilised for both online and offline transactions. | There may be issues related to integration of CBDCs into current payment systems, and their deployment could be expensive and complicated. |
| They can help with cross-border payments, which can be very difficult with conventional fiat currency. | The possibility that CBDCs will negatively affect the banking industry is another possible disadvantage. CBDCs might become more competitive with banks, which could result in lowering bank profits. |
| They can offer financial inclusion to people who are underbanked or unbanked.CBDCs can facilitate people’s access to financial services and participation in the digital economy by offering a digital substitute for cash. | Monetary policy may be negatively impacted by CBDCs. The usage of CBDCs may restrict the central bank’s capacity to carry out monetary policy, which could result in higher inflation or other economic issues. |
Trends and Predictions
When we look at the future of money and the global financial system, CBDCs are expected to play a vital role. The implementation and regulation of CBDCs by the central bank will be crucial in terms of stability and financial system integration. If a country grants all the permissions, CBDC can play a key role in bringing new members and giving them access to the ecosystem in the emerging Web3. In such countries like India, CBDC can witness significant traction as it has already surpassed the milestone of 5 million users in the pilot phase.
As more developed nations are coming forward in support, there will probably be a significant breakthrough in the adoption of CBDCs. A digital euro is one of the many CBDC ideas that the European Central Bank is actively considering in order to improve the payment system and financial inclusion.
Moreover, CBDCs are anticipated to come out as a simple mode of cross-border payment. The Bank of International Settlements (BIS), the Bank of Thailand, the Central Bank of the United Arab Emirates, the Digital Currency Institute of the People’s Bank of China, and the Hong Kong Monetary Authority have collaborated on Project mBridge, an example of such an endeavor.
Conclusion
With the inherent advantages of blockchain technology, CBDCs have the potential to bring a new perspective to the conventional idea of money as state-backed fiat currency. To reduce issues and maximise the advantages of CBDCs, it will be crucial to move ahead cautiously considering all its aspects thoroughly.
It is anticipated that as technology is developing and the global financial systems are changing gradually, CBDCs will be embraced globally. Policymakers, financial institutions, and retailers must stay updated on CBDC for possible monetary gains in the future.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What are Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)?
CBDCs represent the digital counterpart of the local currency and are safeguarded and controlled by a country’s central bank. On the other hand, cryptocurrencies lack this government backing and are not controlled by any central body.
2. Why are countries adopting CBDCs?
Countries are motivated to adopt CBDCs to improve payment efficiency, financial inclusion, cross-border transaction speed, and financial transparency. They also aim to combat criminal activities and reduce reliance on cash.
3. How technology is used in CBDCs?
CBDCs make use of a range of technologies including distributed ledger technology (DLT), smart contracts, cloud infrastructure, encryption technology such as cryptography, and digital identity services like KYC or biometric checks, which guarantee a secure and scalable system as well as effective performance.
4. Which countries are leading in CBDC development?
China is leading in this field by deploying its digital Yuan (e-CNY), followed by Nigeria which has issued the eNaira to facilitate financial access. The European Central Bank is in discussion with the authorities of all euro member states on the possible issuance of a digital Euro, and mBridge and other initiatives encompass several countries to enable cross border payments.
5. What are potential benefits of CBDCs?
CBDCs have the potential of achieving financial inclusion, minimisation of transaction costs, and provision of secure cross border payment, increased efficiency of payment systems and improved transparency of the financial system.
6. What are the challenges CBDCs face?
Aspects such as privacy issues, the risk of cyber attacks, high cost of implementation, and potential negative impacts on legacy banking systems, are some of the main challenges. Transparency and user privacy are still some of the major challenges that need to be addressed.
7. Are CBDCs Secure?
Yes, encryption technology such as public-private keys and zero-knowledge proofs ensure that the transactions as well as personal information remain secure within the CBDC ecosystem.
————————————————————————————————————-
Author: Olumide Ogunjobi
Organization: The Crypto Times
Author Bio: Olumide Ogunjobi is an experienced crypto content writer specializing in DeFi and cryptocurrency research. He excels at creating insightful narratives that simplify complex concepts with precision and clarity.





Be First to Comment