Are you the one who thinks cybersecurity only matters for big corporations and tech companies? It’s time to wake up and smell the malware.
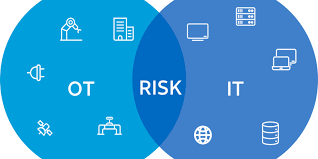
Just because you’re not working at a high-profile company or running a Fortune 500 business doesn’t mean you’re safe from cyber attacks. If you work in the Operational Technology (OT) world, you may be at even greater risk.
OT refers to the hardware and software systems that control the physical processes of a company, such as manufacturing, energy production, or transportation. These systems are becoming increasingly connected to the internet, which means they’re also becoming more vulnerable to hackers.
But don’t panic just yet. In this article, we’ll explain why OT security matters more than ever and what you can do to keep your systems safe. So buckle up and get ready to become an OT security pro.
OT Systems: What Are They and Why Do They Matter?
These days, it’s always important to be aware of security, but the stakes couldn’t be higher regarding Operational Technology (OT) systems. But what exactly are OT systems, and why do they matter? Let’s take a look.
OT systems are a combination of hardware and software used to control and monitor physical production processes. This includes anything from factory automation to production line machines or process control systems. In short, we rely on these systems for efficient business functions and operations across industries.
But the increasing reliance on digital technology means that OT systems have become vulnerable to cyber attacks. If these are compromised, the results can range from costly downtime to significant safety risks. To protect against this, companies need comprehensive cybersecurity strategies with increased monitoring of their OT systems—and this is precisely why OT security matters more than ever before.
What You Should Know About the Future of OT Security
Now that you understand the importance of OT security, it’s time to look toward the future. With technology constantly evolving, the need for strong OT security measures will only continue to grow. Here are some things that need to be done to ensure the future of OT security:
Collaboration
Collaboration between the IT and OT departments will be crucial in the future of OT security. With the increasing number of connected devices, both departments must work together to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. By combining their expertise and resources, organizations can develop comprehensive security strategies encompassing information and operational technology domains.
Continuous monitoring
Continuous monitoring of networks and devices will become the norm in the future of OT security. This goes beyond simply monitoring for threats; it also involves monitoring for any changes in the network that could indicate a potential security issue. Real-time monitoring and analysis will allow organizations to promptly detect and respond to emerging threats, minimizing the potential impact of security incidents.
Education
Education will be vital in ensuring a secure future for OT security. Employees must understand the importance of OT security and be equipped to identify potential threats. Regular training sessions and awareness campaigns are pivotal in cultivating a culture of security awareness and preventing security breaches. By investing in employee education, enterprises can strengthen their defense against evolving cyber threats in the OT security landscape.
Automation
Automation will have a significant impact on OT security in the future. As the number of connected devices grows, it will become increasingly challenging for humans to monitor and respond to potential threats manually. Automation technologies, such as AI and machine learning, can help detect and respond to threats quickly and efficiently, augmenting human efforts and improving overall security.
Staying Informed and Proactive
Organizations must stay informed and proactive in the face of constantly evolving technology and potential threats. Keeping up with the latest trends, technologies, and best practices in OT security is crucial for maintaining a solid and secure OT infrastructure. Regularly assessing and updating security measures, staying aware of emerging threats, and adapting to regulatory changes will help organizations stay ahead and ensure the future of OT security remains robust.
By embracing collaboration, continuous monitoring, education, and automation, organizations can build a strong foundation for the future of OT security. Being proactive and staying informed about emerging technologies and potential threats will be key to protecting critical infrastructure and ensuring the resilience of OT networks.
Emerging Technologies Improving OT Cybersecurity
Emerging technologies are strengthening OT cybersecurity, which is essential to understand as we move into the future. One exciting example is the development of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. With these technologies, devices can learn what constitutes “normal” activity on an OT network, recognize anomalies outside of that norm, and flag them for security professionals to investigate. This improves response times and enables a more proactive approach to cybersecurity.
Another emerging technology that’s important for OT security is blockchain. In the industrial world, blockchain can be used to verify the authenticity of data from connected devices or sensors in real-time by creating a secure network of trust between parties involved with the supply chain and production systems. This helps prevent unauthorized access to or tampering with sensitive data.
New efforts are underway to improve protocols for securing IoT devices connected to OT networks. As these devices become more commonplace in industrial settings, they pose a greater risk for potential cyber-attacks. But with better IoT security protocols—including more substantial encryption standards, two-factor authentication, and device management tools—companies can more easily manage these risks.
In short, as technology advances, so does our ability to protect OT systems from cyber threats. By staying informed about emerging technologies and incorporating them into their overall cybersecurity strategies, organizations can create a safer future for industrial networks.
Best Practices for Improving OT Cybersecurity
Remember a few best practices when securing your OT (operational technology) systems.
- First and foremost, ensure you thoroughly understand your network and all its connected devices. This will help you identify and address potential vulnerabilities before cyber attackers can exploit them.
- Another critical step is to implement strong access controls and authentication protocols. This means using strong passwords (or, even better, multi-factor authentication) for all users and limiting access to critical systems only to those who need it.
- Regularly monitoring your network and systems is crucial as well. This can help you detect any anomalous or suspicious activity early on, allowing you to take action before any real damage is done.
- Finally, it’s essential to have a solid incident response plan in place in case of a cyber attack. This means having the right tools and technologies to detect and respond to threats and having a clear plan of action that outlines who does what in the event of an attack.
By following these best practices, you can help ensure that your OT systems remain secure and protected from cyber threats now and into the future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, as technology advances and more systems become connected, the importance of OT security cannot be overstated. Cyber attacks on industrial systems can cause devastating consequences, from financial losses to physical harm.
Companies must prioritize OT security and implement measures to protect their systems from cyber threats. This includes technical solutions like firewalls and intrusion detection systems and employee education and training on best practices for cybersecurity.
Remember, OT security is not the same as IT security. It requires a specialized approach and understanding of industrial systems’ unique challenges and risks. By taking proactive steps to secure their OT systems, companies can ensure the safety and reliability of their operations and protect themselves from the costly consequences of cyber attacks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is OT security?
Defending operational technology (OT) networks from cyber threats is called OT security. This comprises supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, distributed control systems (DCS), programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and other related technologies. These networks monitor and regulate physical processes in various industries, including manufacturing, energy generation, transportation, and healthcare.
What are the difficulties in securing OT networks?
Because of their complexity and diversity, OT networks can be challenging to secure. Many of these systems were created without consideration for cybersecurity, making them open to attack. Furthermore, many firms need more visibility into their OT environments due to insufficient monitoring capabilities or a lack of cybersecurity resources. As a result, organizations may need help recognizing potential dangers before they become a problem.
How can businesses improve their OT security positioning?
Organizations should improve their overall security posture by implementing best practices such as network segmentation, deploying secure remote access solutions, conducting regular vulnerability assessments, patching regularly, implementing robust authentication protocols, and utilizing advanced analytics tools for threat detection and response. Furthermore, organizations should consider investing in specialist training programs for staff who deal with or manage these systems to understand better how to best secure them from cyber threats.



Be First to Comment